See Roots of Public speaking here
Roots of Public Speaking
Ancient Greece
Why was public speaking considered so important to the ancient Greeks?
born 384 BC, died 322 BC
. Founded the Lyceum
in Athens the third century BC.
Rhetoric means:
“Finding all of the available
means of persuasion.”
Effective rhetoric requires
“a study of the human soul.”
Adapting your message to meet
the needs of the audience.
· Aristotle’s model of communication:
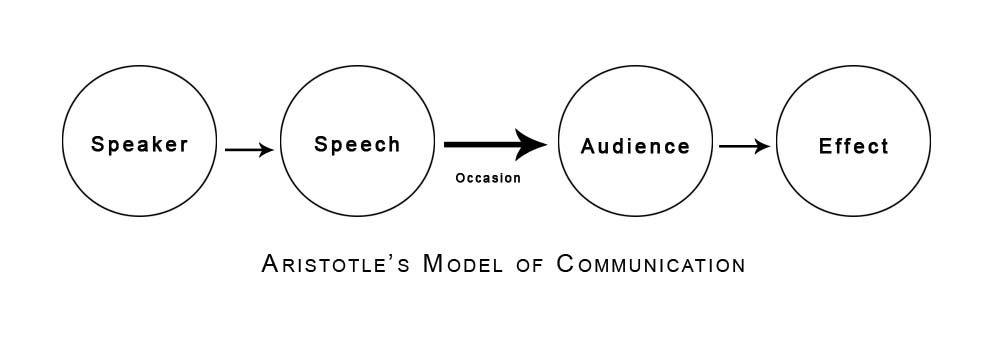
Applied to the
Cannons of Rhetoric
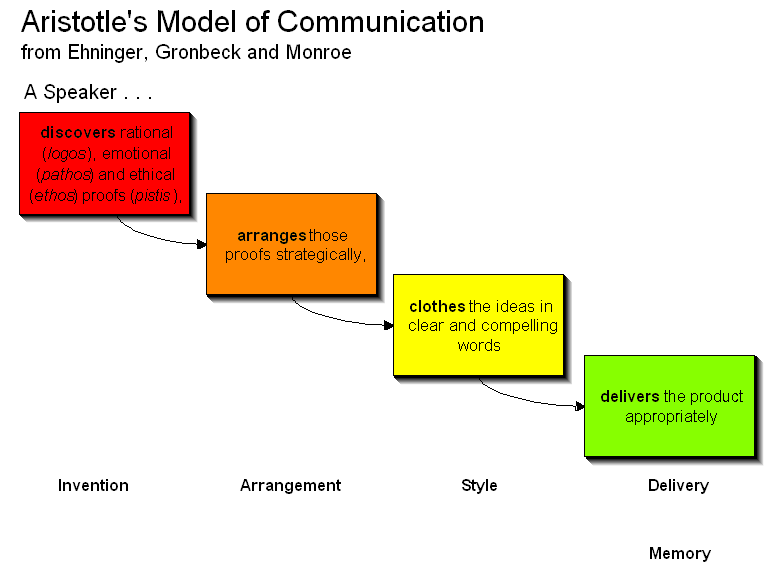
·Three types of classical Greek public
speeches:
Forensic— for courts
— issue of Fact
— concerned with past
Example: trial of Socrates
Deliberative— for the assembly (legislature)
— issue of Policy
— concerned with future
Example of Thatcher in Parliament
Epideictic
— for ceremony
— issue of Value
— concerned with present
Example of Martin Luther King
Modern version:
three basic types of
speeches
Speeches to inform
Goal is to help the audience understand and remember
Speeches to persuade

Goal is to change attitudes, beliefs or actions.
Speeches to evoke
Goal is to catch and keep attention or to enhance self definitions of audience.
Aristotle said that rhetoric has “three divisions — (1) the speaker’s power of evincing a personal character which will make his speech credible (ethos );
(2) his power of stirring the emotions of his hearers (pathos ); (3) his power of proving a truth, or an apparent truth, by means of persuasive arguments (logos ).”
· The Three Classical Proofs
Logos — (logic) Source of
the persuasion for logos is in
the speech
Pathos — (passion) Source
of persuasion for pathos is in
the audience
Ethos — (credibility)
Source of the persuasion for
ethos is in the speaker
Ethos is the character appeal
of speaker. Trustworthiness.
· Kenneth Burke, 1897 — 1993
“The Rhetoric of Motives.”
Goal of communication is to achieve Identification
Finding Common Ground. Sharing self definitions.
“The sharing of substance.” — Burke
Types of identification:
Rite of passage experience
Geography
Nationality
Group membership
Religion
Language
Shared values and beliefs
Three levels of identification in public speaking. :
1. Audience identifies with speaker.
2. Audience identifies with topic. “Salience.”
3. Topic identifies with situation.
“Right thing spoken at the right time.”
PowerPoint Karaoke
First student
1. Planning a vacation. 2. Pranks.
Second student
1. Proper bathroom etiquette. 2. Hazards of social networking.
Third student
1. Seattle coffee culture. 2. Long van rides.
Fourth student
1. Leprechauns vs Easter bunnies. 2. Hipster pastors
Fifth student
1. Student government fiascos 2. Waking up is hard to do.
_________________________________________
http://www.slideteam.net/media/catalog/product/cache/1/image/9df78eab33525d08d6e5fb8d27136e95/3/d/3d_pyramid_5_pieces_powerpoint_presentation_slides_Slide01.jpg
http://blog.haikudeck.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/PPT_Vordek.jpg http://www.http://www.myinterestingfacts.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/Human-Body.jpgslideteam.net/media/catalog/product/cache/1/image/9df78eab33525d08d6e5fb8d27136e95/v/e/venn_diagram_4_pieces_powerpoint_presentation_slides_Slide01.jpg
http://images4.fanpop.com/image/photos/23400000/Wake-Up-Kitty-Video-He-really-says-that-wake-up-kitty-videos-23448561-1167-844.jpg
http://www.mysteriousexhortations.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/A70-2923.jpeg http://assets.rollingstone.com/assets/2015/article/justin-bieber-comedy-central-roast-20150120/182017/medium_rect/1421760679/720×405-455084116.jpg http://www.higheredlive.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/bright-future-ahead.jpg
PowerPoint Karaoke
Frist student
1. Planning a vacation. 2. Pranks.
Second student
1. Proper bathroom etiquette. 2. Hazards of social networking.
Third student
1. Seattle coffee culture. 2. Long van rides.
Fourth student
1. Leprechauns vs Easter bunnies. 2. Hipster pastors
Fifth student
1. Student government fiascos 2. Waking up is hard to do. |


No comments:
Post a Comment